How To Set Log Scale In Matlab
Hello programmers, in today's article, nosotros will learn well-nigh the Matplotlib Logscale in Python. Matplotlib log scale is a scale having powers of 10. You could use any base of operations, like 2, or the natural logarithm value is given by the number e. Using different bases would narrow or widen the spacing of the plotted elements, making visibility easier. We tin can use the Matlplotlib log calibration for plotting axes, histograms, 3D plots, etc. Let'southward take a wait at different examples and implementations of the log scale.
Logarithmic Scales are a very important data visualization technique. This calibration allows us to witness the exponential growth of a organisation on a linear scale. For instance, the cases of Novel Corona Virus are increasing in an exponential style, In such cases, using log scales helps you to cheque the command of the virus.
Changing y-axis to Matplotlib log calibration
from matplotlib import pyplot # Create a subplot to show the graph pyplot.subplot(1, 1, 1) # Powers of ten a = [10**i for i in range(10)] # Plotting the graph pyplot.plot(a, color='blue', lw=ii) # Setting a logarithmic calibration for y-axis pyplot.yscale('log') pyplot.show() Output:
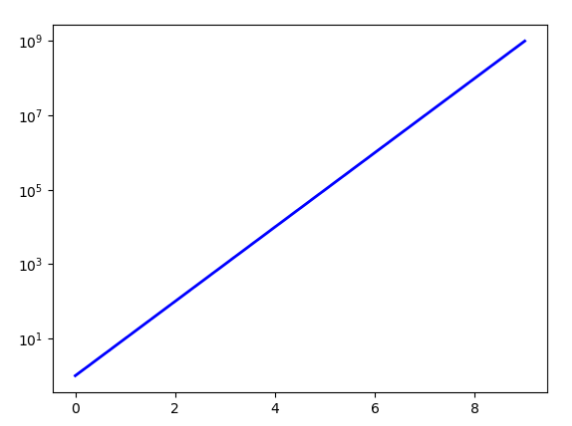
Explanation:
The process of plot logarithmic axes is similar to regular plotting, except for one line of code specifying the type of axes equally 'log.' In the above example, nosotros outset set upwards the subplot required plot the graph. We will then plot the powers of 10 confronting their exponents. This is a linear, logarithmic graph. Without the logarithmic scale, the information plotted would show a curve with an exponential rise. Thus to obtain the y-centrality in log calibration, we volition accept to laissez passer 'log' as an statement to the pyplot.yscale(). Similarly, y'all tin utilize the same to change the x-centrality to log calibration by using pyplot.xscale('log')
Matplotlib Log Scale Using Semilogx() or Semilogy() functions
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot equally plt 10 = [10, 100, thou, 10000, 100000] y = [2, 4 ,8, sixteen, 32] fig = plt.figure(figsize=(eight, 6)) plt.scatter(ten,y) plt.plot(10,y) plt.grid() plt.semilogx() plt.semilogy(basey=two) plt.xlabel("x",fontsize=20) plt.ylabel("y",fontsize=20) plt.testify() Output:
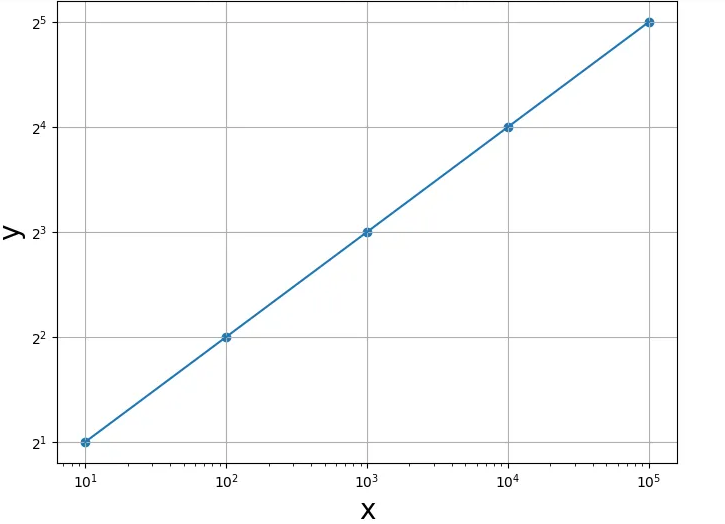
Caption:
Thesemilogx() function is some other method of creating a plot with log scaling along the 10-axis. While the semilogy() function creates a plot with log scaling along Y-centrality. The default base of the logarithm is ten. We tin, nonetheless, prepare the base with basex and basey parameters for the role semilogx() and semilogy(), respectively. In the above example, the plt.semilogx() office with default base of operations 10 is used to change the 10-axis to a logarithmic calibration. While the plt.semilogy() function changes the y-axis to base two log scale.
Matplotlib Log Calibration Using loglog() function
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = [10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000] y = [ii, iv ,viii, 16, 32] fig = plt.effigy(figsize=(8, vi)) plt.scatter(ten,y) plt.plot(ten,y) plt.loglog(basex=10,basey=2) plt.testify() Output:
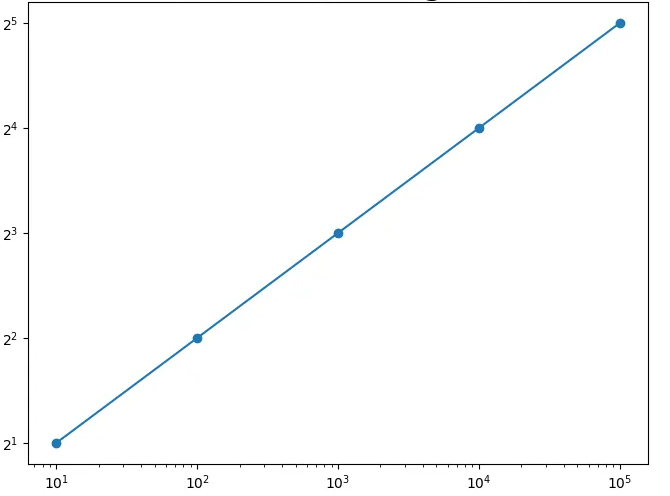
Caption:
We can also implement log scaling forth both X and Y axes by using theloglog() function. The base of the logarithm for the X-centrality and Y-axis is set by basex and basey parameters. In the to a higher place instance, basex = 10 and basey = 2 is passed as arguments to the plt.loglog() function which returns the base 10 log scaling ten-centrality. And base of operations ii log scaling along the y-axis.
Scatter plot with Matplotlib log scale in Python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy every bit np f, ax = plt.subplots() ax.set_xscale('log') ax.set_yscale('log') ax.scatter(two**np.arange(10), 2**np.arange(10)) Output:
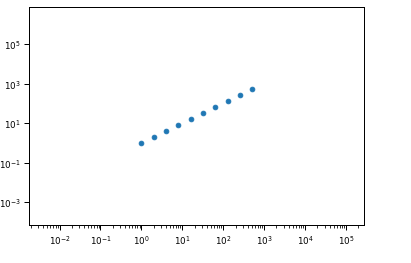
Caption:
In the above example, the axes are the first log scaled, bypassing 'log' every bit a parameter to the ser_xscale() and set_yscale() functions. The plt.scatter() office is then chosen, which returns the scatter plot on a logarithmic calibration. The margins of the plot are huge. Yet, if the plt.besprinkle() method is used before log scaling the axes, the scatter plot appears normal.
Matplotlib logscale Histogram Plot
<pre class="wp-block-syntaxhighlighter-code">import pandas as pd import numpy every bit np import matplotlib.pyplot every bit plt ten = [2, 1, 76, 140, 286, 267, 60, 271, 5, 13, 9, 76, 77, 6, 2, 27, 22, 1, 12, 7, xix, 81, 11, 173, 13, 7, 16, 19, 23, 197, 167, one] ten = pd.Series(x) # <a href="https://world wide web.pythonpool.com/matplotlib-2d-histogram/" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">histogram</a> on linear calibration plt.subplot(211) hist, bins, _ = plt.hist(ten, bins=8) # histogram on log scale. # Employ non-equal bin sizes, such that they look equal on log scale. logbins = np.logspace(np.log10(bins[0]),np.log10(bins[-one]),len(bins)) plt.subplot(212) plt.hist(10, bins=logbins) plt.xscale('log') plt.prove()</pre> Output:
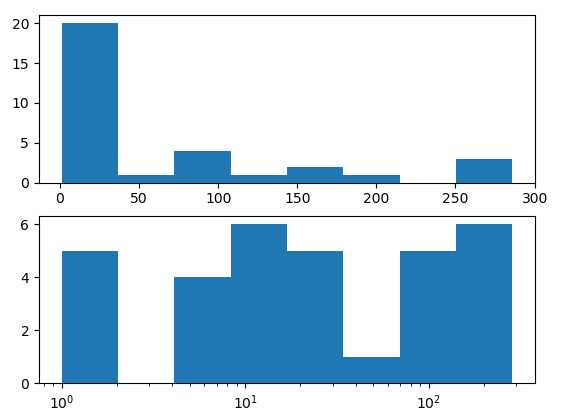
Explanation:
In the in a higher place example, the Histogram plot is once fabricated on a normal calibration. And likewise plotted on Matplotlib log calibration. For plotting histogram on a logarithmic scale, the bins are divers as 'logbins.' Also, we use non-equal bin sizes, such that they look equal on a log scale. The x-axis is log scaled, bypassing 'log' as an argument to the plt.xscale() function.
How to Plot Negative Values on Matplotlib Logscale?
Sometimes, your data contains both positive and negative values. In such scenarios, the log scale won't work since log values of negative numbers doesnt exists. In such cases, we have couple of options to follow –
- Shift the origin to the lowest value of the dataset. This means the lowest value in your dataset will become 0 and every other value volition exist increased by the absolute of your everyman value. arr = arr + min(arr) will give yous the non negative values.
- Using Symmetric Log Scale. This scale will value both sides of 0. Use plt.yscale('symlog') to apply a symmetric log scale on the yaxis.
Conclusion:
In this article, we accept discussed various ways of changing into a logarithmic scale using the Matplotlib logscale in Python. We have seen different functions to implement log scaling to axes. Like semilogx() or semilogy() functions and loglog() functions. Nosotros likewise cited examples of using Matplotlib logscale to plot to scatter plots and histograms. Refer to this commodity in case of any queries regarding the utilise of Matplotlib Logscale.
Still, if you accept any doubts or questions, do permit me know in the annotate section below. I will try to help yous as shortly as possible.
Happy Pythoning!
Source: https://www.pythonpool.com/matplotlib-log-scale/

0 Response to "How To Set Log Scale In Matlab"
Post a Comment